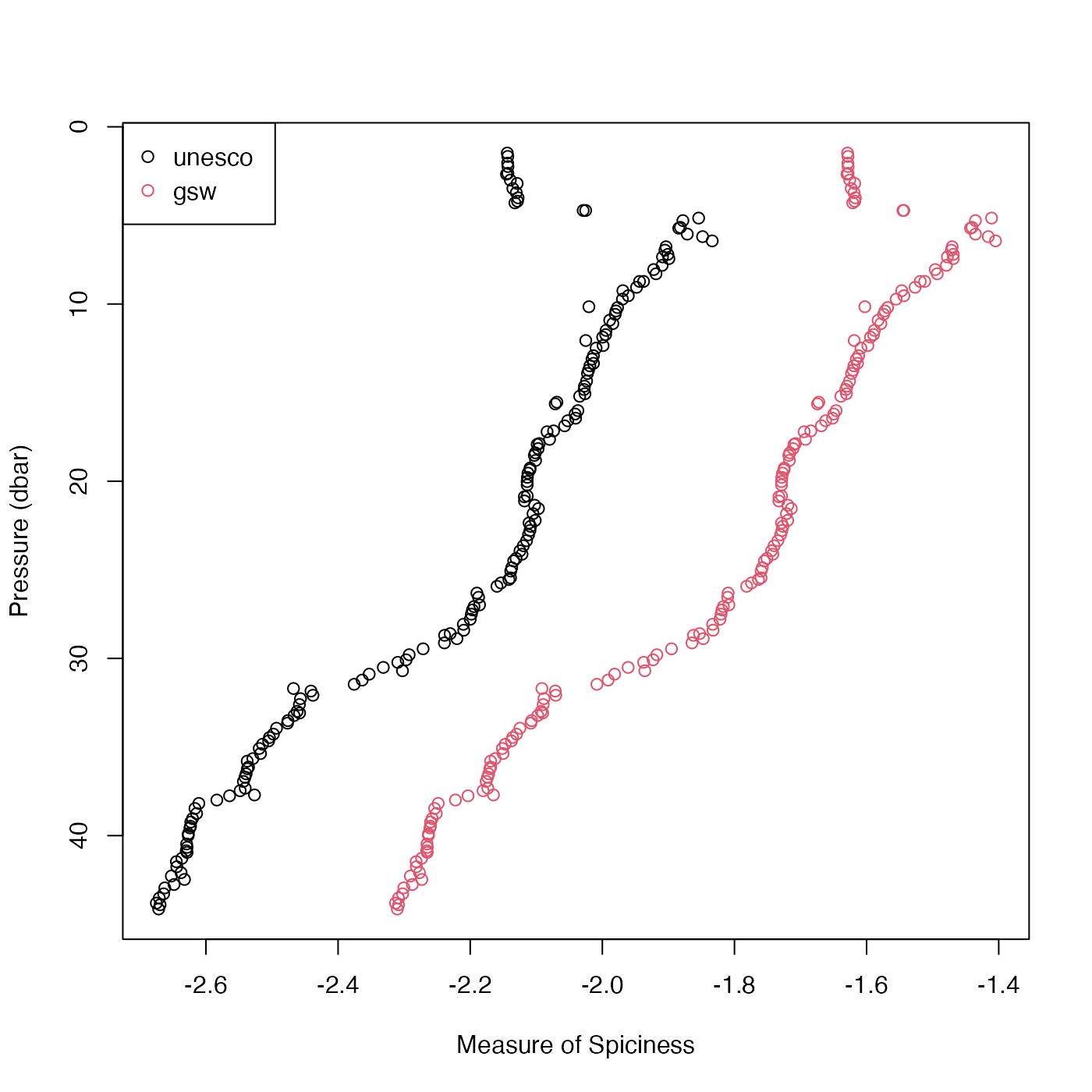
Compute seawater "spice", a variable that is in some sense orthogonal to
density in TS space. Larger spice values correspond to relative warm and
salty water, compared with smaller spice values. Two distinct variants exist.
If eos="unesco" then Flament's (2002) formulation is used. If eos="gsw"
then gsw::gsw_spiciness0() is used to compute a newer variant that is part
of the Gibbs SeaWater formulation (McDougall and Krzysik, 2015). See the
“Examples” section for a graphical illustration of the difference in a
typical coastal case.
Arguments
- salinity
either salinity (PSU) (in which case
temperatureandpressuremust be provided) or actdobject (in which casesalinity,temperatureandpressureare determined from the object, and must not be provided in the argument list).- temperature
in-situ temperature (\(^\circ\)C) on the ITS-90 scale; see “Temperature units” in the documentation for
swRho().- pressure
Seawater pressure (dbar) (only used if
eosis"gsw"); see “Details”..- longitude
longitude of observation (only used if
eosis"gsw"; see “Details”).- latitude
latitude of observation (only used if
eosis"gsw"; see “Details”).- eos
Character value specifying the equation of state, either
"unesco"(for the Flament formulation, although this is not actually part of UNESCO) or"gsw"for the Gibbs SeaWater formulation.- debug
an integer specifying whether debugging information is to be printed during the processing. This is a general parameter that is used by many
ocefunctions. Generally, settingdebug=0turns off the printing, while higher values suggest that more information be printed. If one function calls another, it usually reduces the value ofdebugfirst, so that a user can often obtain deeper debugging by specifying higherdebugvalues.
Value
Flament-formulated spice \(kg/m^3\) if eos is "unesco"
or surface-referenced GSW spiciness0 \(kg/m^3\) if eos is "gsw",
the latter provided by gsw::gsw_spiciness0(), and hence aimed
at application within the top half-kilometre of the ocean.
Details
If the first argument is a ctd object, then salinity, temperature and
pressure values are extracted from it, and used for the calculation. For
the eos="gsw" case, longitude and latitude are also extracted, because
these are required by gsw::gsw_spiciness0().
Roughly speaking, seawater with a high spiciness is relatively warm and salty compared with less spicy water. Another interpretation is that spice is a variable measuring distance orthogonal to isopycnal lines on TS diagrams (if the diagrams are scaled to make the isopycnals run at 45 degrees). Note that pressure, longitude and latitude are all ignored in the Flament definition.
References
Flament, P. “A State Variable for Characterizing Water Masses and Their Diffusive Stability: Spiciness.” Progress in Oceanography, Observations of the 1997-98 El Nino along the West Coast of North America, 54, no. 1 (July 1, 2002):493-501. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(02)00065-4
McDougall, Trevor J., and Oliver A. Krzysik. “Spiciness.” Journal of Marine Research 73, no. 5 (September 1, 2015): 141-52.
See also
Other functions that calculate seawater spiciness:
swSpiciness0(),
swSpiciness1(),
swSpiciness2()
Other functions that calculate seawater properties:
T68fromT90(),
T90fromT48(),
T90fromT68(),
computableWaterProperties(),
locationForGsw(),
swAbsoluteSalinity(),
swAlpha(),
swAlphaOverBeta(),
swBeta(),
swCSTp(),
swConservativeTemperature(),
swDepth(),
swDynamicHeight(),
swLapseRate(),
swN2(),
swPressure(),
swRho(),
swRrho(),
swSCTp(),
swSR(),
swSTrho(),
swSigma(),
swSigma0(),
swSigma1(),
swSigma2(),
swSigma3(),
swSigma4(),
swSigmaT(),
swSigmaTheta(),
swSoundAbsorption(),
swSoundSpeed(),
swSpecificHeat(),
swSpiciness0(),
swSpiciness1(),
swSpiciness2(),
swSstar(),
swTFreeze(),
swTSrho(),
swThermalConductivity(),
swTheta(),
swViscosity(),
swZ()
Examples
# Compare unesco and gsw formulations
library(oce)
data(ctd)
p <- ctd[["pressure"]]
U <- swSpice(ctd, eos = "unesco")
G <- swSpice(ctd, eos = "gsw")
xlim <- range(c(U, G), na.rm = TRUE)
ylim <- rev(range(p))
plot(U, p,
xlim = xlim, ylim = ylim,
xlab = "Measure of Spiciness", ylab = "Pressure (dbar)"
)
points(G, p, col = 2)
legend("topleft", col = 1:2, pch = 1, legend = c("unesco", "gsw"))