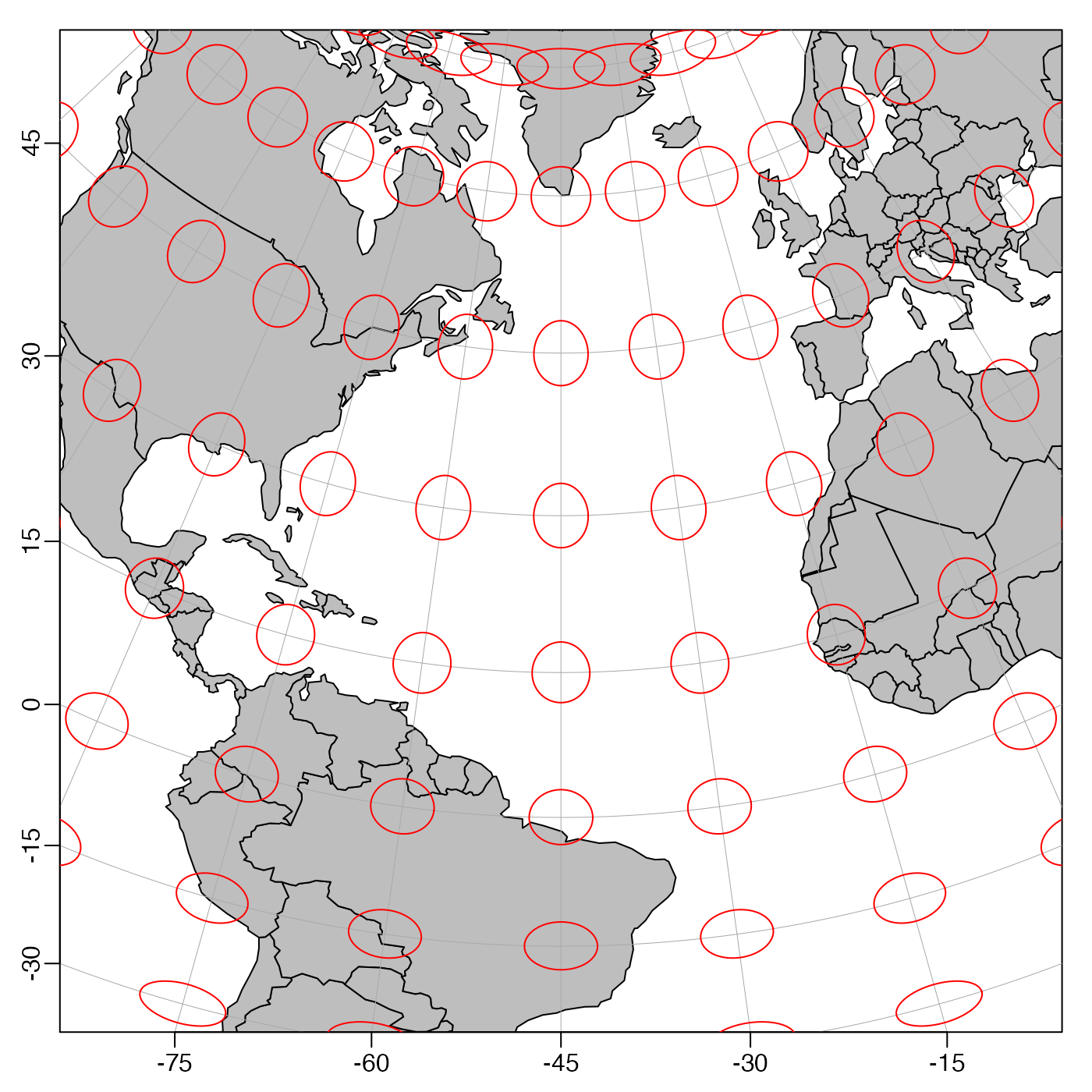
Plot ellipses at grid intersection points, as a method for indicating the distortion inherent in the projection, somewhat analogous to the scheme used in reference 1. (Each ellipse is drawn with 64 segments.)
Usage
mapTissot(grid = rep(15, 2), scale = 0.2, crosshairs = FALSE, ...)Arguments
- grid
numeric vector of length 2, specifying the increment in longitude and latitude for the grid. Indicatrices are drawn at e.g. longitudes
seq(-180, 180, grid[1]).- scale
numerical scale factor for ellipses. This is multiplied by
min(grid)and the result is the radius of the circle on the earth, in latitude degrees.- crosshairs
logical value indicating whether to draw constant-latitude and constant-longitude crosshairs within the ellipses. (These are drawn with 10 line segments each.) This can be helpful in cases where it is not desired to use
mapGrid()to draw the longitude/latitude grid.- ...
extra arguments passed to plotting functions, e.g.
col="red"yields red indicatrices.
See also
A map must first have been created with mapPlot().
Other functions related to maps:
formatPosition(),
lonlat2map(),
lonlat2utm(),
map2lonlat(),
mapArrows(),
mapAxis(),
mapContour(),
mapCoordinateSystem(),
mapDirectionField(),
mapGrid(),
mapImage(),
mapLines(),
mapLocator(),
mapLongitudeLatitudeXY(),
mapPlot(),
mapPoints(),
mapPolygon(),
mapScalebar(),
mapText(),
oceCRS(),
oceProject(),
shiftLongitude(),
usrLonLat(),
utm2lonlat()