Smooth a section, in any of several ways, working either in the vertical direction or in both the vertical and lateral directions.
Usage
sectionSmooth(
section,
method = "spline",
x,
xg,
yg,
xgl,
ygl,
xr,
yr,
df,
gamma = 0.5,
iterations = 2,
trim = 0,
pregrid = FALSE,
debug = getOption("oceDebug"),
...
)Arguments
- section
A
sectionobject containing the section to be smoothed. Formethod="spline", the pressure levels must match for each station in the section.- method
A string or a function that specifies the method to use; see “Details”.
- x
Optional numerical vector, of the same length as the number of stations in
section, which will be used in gridding in the lateral direction. If not provided, this defaults togeodDist(section).- xg, xgl
ignored in the
method="spline"case, but passed tointerpBarnes()ifmethod="barnes", to kriging functions ifmethod="kriging", or tomethoditself, if it is a function. Ifxgis supplied, it defines the x component of the grid, which by default is the terms of station distances, x, along the track of the section. (Note that the gridxgis trimmed to the range of the datax, because otherwise it would be impossible to interpolate between stations to infer water depth, longitude, and latitude, which are all stored within the stations in the returnedsectionobject.) Alternatively, ifxglis supplied, the x grid is established usingseq(), to span the data withxglelements. If neither of these is supplied, the output x grid will equal the input x grid.- yg, ygl
similar to
xgandxgl, but for pressure. (Note that trimming to the inputyis not done, as it is forxgandx.) Ifygis not given, it is determined from the deepest station in the section. Ifyglwas not given, then a grid is constructed to span the pressures of that deepest station withyglelements. On the other hand, ifyglwas not given, then the y grid will constructed from the pressure levels in the deepest station.- xr, yr
influence ranges in x (along-section distance) and y (pressure), passed to
interpBarnes()ifmethod="barnes"or tomethod, if the latter is a function. If missing,xrdefaults to 1.5X the median inter-station distance andyrdefaults to 0.2X the pressure range. Since these defaults have changed over the evolution ofsectionSmooth, analysts ought to supplyxrandyrin the function call, tailoring them to particular applications, and making the code more resistant to changes insectionSmooth.- df
Degree-of-freedom parameter, passed to
smooth.spline()ifmethod="spline", and ignored otherwise. Ifdfis not provided, it defaults to 1/5-th of the number of stations containing non-NAdata at the particular pressure level being processed, assectionSmoothworks its way through the water column.- gamma, iterations, trim, pregrid
Values passed to
interpBarnes(), ifmethod="barnes", and ignored otherwise.gammais the factor by whichxrandyrare reduced on each of succeeding iterations.iterationsis the number of iterations to do.trimcontrols whether the gridded data are set toNAin regions with sparse data coverage.pregridcontrols whether data are to be pre-gridded withbinMean2D()before being passed tointerpBarnes().- debug
A flag that turns on debugging. Set to 1 to get a moderate amount of debugging information, or to 2 to get more.
- ...
Optional extra arguments, passed to either
smooth.spline(), ifmethod="spline", and ignored otherwise.
Value
A section object of that has been smoothed in some way.
Every data field that is in even a single station of the input object
is inserted into every station in the returned value, and therefore
the units represent all the units in any of the stations, as do the
flag names. However, the flags are all set to NA values.
Details
This function produces smoothed fields that might be useful in
simplifying graphical elements created with plot,section-method().
As with any smoothing method, a careful analyst will compare the results
against the raw data, e.g. using plot,section-method().
In addition the problem of falsely widening narrow features such as
fronts, there is also the potential to get unphysical results with
spars sampling near topographic features such as bottom slopes and ridges.
The method argument selects between three possible methods.
For
method="spline", i.e. the default, the section is smoothed laterally, usingsmooth.spline()on individual pressure levels. (If the pressure levels do not match up,sectionGrid()should be used first to create asectionobject that can be used here.) Thedfargument sets the degree of freedom of the spline, with larger values indicating less smoothing.For
method="barnes", smoothing is done across both horizontal and vertical coordinates, usinginterpBarnes(). The output station locations are computed by linear interpolation of input locations, usingapprox()on the original longitudes and longitudes of stations, with the independent variable being the distance along the track, computed withgeodDist(). The values ofxg,yg,xglandyglcontrol the smoothing.For
method="kriging", an error is reported. This is because the code formerly used the automap package, but this was removed from CRAN in June 2025.If
methodis a function, then that function is applied to the (distance, pressure) data for each variable at a grid defined byxg,xgl,ygandygl. The function must be of the formfunction(x,y,z,xg,xr,yg,yr), and must return a matrix of the gridded result, with first index indicating the "grid" station number and second index indicating "grid" pressure. Thexvalue that is supplied to this function is set as the distance along the section, as computed withgeodDist(), and repeated for each of the points at each station. The corresponding pressures are provided iny, and the value to be gridded is inz, which may betemperatureon one call to the function,salinityon another call, etc. The other quantities have the meanings as described below.
See also
Other things related to section data:
[[,section-method,
[[<-,section-method,
as.section(),
handleFlags,section-method,
initializeFlagScheme,section-method,
plot,section-method,
read.section(),
section,
section-class,
sectionAddStation(),
sectionGrid(),
sectionSort(),
subset,section-method,
summary,section-method
Examples
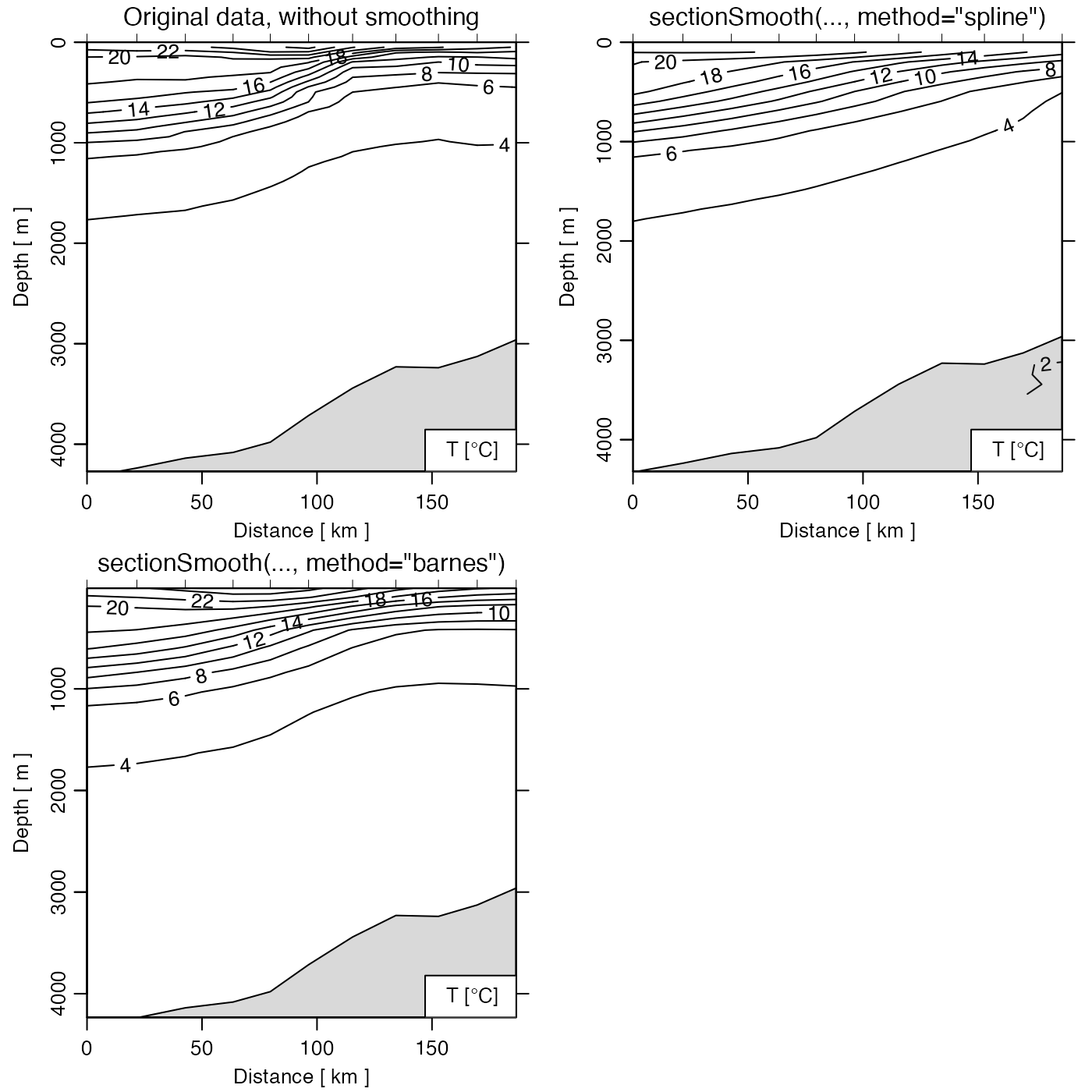
# Unsmoothed (Gulf Stream)
library(oce)
data(section)
gs <- subset(section, 115 <= stationId & stationId <= 125)
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
plot(gs, which = "temperature")
mtext("Original data, without smoothing", line = 0.5)
# Spline
gsg <- sectionGrid(gs, p = seq(0, 5000, 100))
gsSpline <- sectionSmooth(gsg, "spline")
plot(gsSpline, which = "temperature")
mtext("sectionSmooth(..., method=\"spline\")", line = 0.5)
# Barnes
gsBarnes <- sectionSmooth(gs, "barnes", xr = 50, yr = 200)
plot(gsBarnes, which = "temperature")
mtext("sectionSmooth(..., method=\"barnes\")", line = 0.5)