Moon phase calculation
The illuminated fraction of the moon can be calculated with moonAngle() in
the oce package, as illustrated graphically and in R code below.
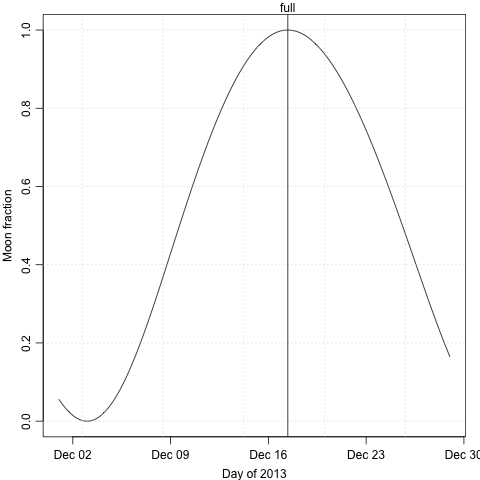
Code
library(oce)
if (!interactive()) png("2013-12-21-moon-phases.png")
par(mar = c(3, 3, 1, 1), mgp = c(2, 0.7, 0)) # tighten margins
t <- as.POSIXct("2013-12-1", tz = "UTC") + seq(0, 28 * 24 * 3600, 3600)
f <- moonAngle(
t = t, longitude = -63.6, latitude = 44.65
)$illuminatedFraction
plot(t, f, type = "l", xlab = "Day of 2013", ylab = "Moon fraction")
grid()
# For interest, add full-moon time as indicated in an almanac.
full <- as.POSIXct("2013-12-17 05:29:00", tz = "America/Halifax")
abline(v = full)
mtext("full", at = full, side = 3)
Exercises (a) Try this for other locations. (b) Detect full moon by using uniroot() on the rate of change of illumination.